当前你的浏览器版本过低,网站已在兼容模式下运行,兼容模式仅提供最小功能支持,网站样式可能显示不正常。
请尽快升级浏览器以体验网站在线编辑、在线运行等功能。
3893:Hard-working Student
题目描述
Billy is a hard-working student. He is fond of computers and intends to learn as much as possible. Now he studies graph theory, and must write a program to build the graph which is shown on the Figure.
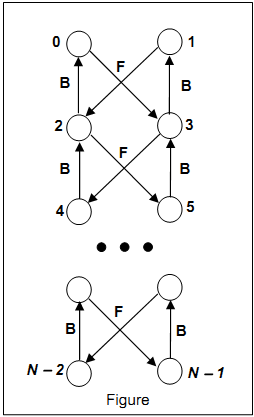
The vertices of the graph are labeled sequentially with integer keys starting from 0 to N - 1 (N≤10000). There are two types of edges: backward edges - labeled with B in the Figure (for example from node 4 to node 2, or from node 3 to node 1), and forward edges, labeled with F in the Figure (for example from node 1 to node 2 or from node 0 to node 3). Billy’s program starts with an initial graph that contains the vertices 0, 1, 2, 3, and must continue to build the graph based on a sequence of commands written in a text file. A command has the following specification:
index0 string_of_characters index1
where index0 and index1 are the keys of vertices, and string_of_characters is a sequence of actions executed from right to left. An action is represented by one of the following characters:
where v is the array of the nodes of the graph. The argument of the first operation is the node v[index1]. The result of the operations f and b is a node that represents the argument for all the other operations. The operations < and = are the leftmost specified. For example, for the command 4 <kff 0 the actions are:
A node is put in the array v only by the command <. Initially the array contains the nodes with keys 0, 1, 2, 3, v[0]=0, v[1]=1,v[2]=2 and v[3]=3.

The vertices of the graph are labeled sequentially with integer keys starting from 0 to N - 1 (N≤10000). There are two types of edges: backward edges - labeled with B in the Figure (for example from node 4 to node 2, or from node 3 to node 1), and forward edges, labeled with F in the Figure (for example from node 1 to node 2 or from node 0 to node 3). Billy’s program starts with an initial graph that contains the vertices 0, 1, 2, 3, and must continue to build the graph based on a sequence of commands written in a text file. A command has the following specification:
where index0 and index1 are the keys of vertices, and string_of_characters is a sequence of actions executed from right to left. An action is represented by one of the following characters:
| Character | Action |
| f | Follow the Forward edge if it does exist or creates it and the corresponding vertex from an argument node |
| b | Follow the backward edge if it does exist or creates it and corresponding vertex, starting from an argument node |
| k | Prints the key of the argument node |
| < | v[index0] = argument node |
| = | Prints ‘=’ if v[index0] == node or ‘#’ otherwise |
where v is the array of the nodes of the graph. The argument of the first operation is the node v[index1]. The result of the operations f and b is a node that represents the argument for all the other operations. The operations < and = are the leftmost specified. For example, for the command 4 <kff 0 the actions are:
index0 = 4, index1 = 0
x = f(v[0]) // forward to node 3, x = 3
y = f(x) // forward creates node (4), y = 4
k(y) // prints the key (4)
V[4] = y // put node (4) in array v
A node is put in the array v only by the command <. Initially the array contains the nodes with keys 0, 1, 2, 3, v[0]=0, v[1]=1,v[2]=2 and v[3]=3.
输入解释
The file contains the sequence of commands. White spaces can occur freely in the input. The input data terminate with an end of file.
输出解释
Each print must be to the standard output from the beginning of a line. There are no empty lines in between.
输入样例
4
输出样例
4 =
最后修改于 2020-10-29T07:14:51+00:00 由爬虫自动更新
共提交 0 次
通过率 --%
| 时间上限 | 内存上限 |
| 1000 | 65536 |
登陆或注册以提交代码