当前你的浏览器版本过低,网站已在兼容模式下运行,兼容模式仅提供最小功能支持,网站样式可能显示不正常。
请尽快升级浏览器以体验网站在线编辑、在线运行等功能。
3810:Hobby on Rails
题目描述
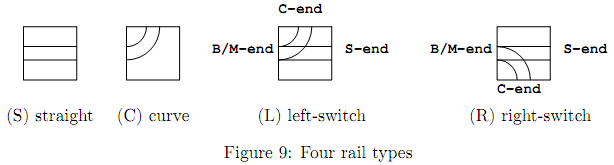
ICPC (International Connecting Points Company) starts to sell a new railway toy. It consists of a toy tramcar and many rail units on square frames of the same size. There are four types of rail units, namely, straight (S), curve (C), left-switch (L) and right-switch (R) as shown in Figure 9. A switch has three ends, namely, branch/merge-end (B/M-end), straight-end (S-end) and curve-end (C-end).
A switch is either in “through” or “branching” state. When the tramcar comes from B/M-end, and if the switch is in the through-state, the tramcar goes through to S-end and the state changes to branching; if the switch is in the branching-state, it branches toward C-end and the state changes to through. When the tramcar comes from S-end or C-end, it goes out from B/M-end regardless of the state. The state does not change in this case.
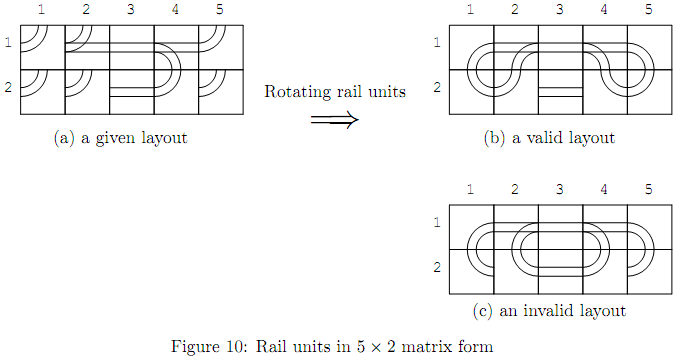
Kids are given rail units of various types that fill a rectangle area of w * h, as shown in Figure 10(a). Rail units meeting at an edge of adjacent two frames are automatically connected. Each rail unit may be independently rotated around the center of its frame by multiples of 90 degrees in order to change the connection of rail units, but its position cannot be changed.
Kids should make “valid” layouts by rotating each rail unit, such as getting Figure 10(b) from Figure 10(a). A layout is valid when all rails at three ends of every switch are directly or indirectly connected to an end of another switch or itself. A layout in Figure 10(c) is invalid as well as Figure 10(a). Invalid layouts are frowned upon.
When a tramcar runs in a valid layout, it will eventually begin to repeat the same route forever. That is, we will eventually find the tramcar periodically comes to the same running condition, which is a triple of the tramcar position in the rectangle area, its direction, and the set of the states of all the switches.
A periodical route is a sequence of rail units on which the tramcar starts from a rail unit with a running condition and returns to the same rail unit with the same running condition for the first time. A periodical route through a switch or switches is called the “fun route”, since kids like the rattling sound the tramcar makes when it passes through a switch. The tramcar takes the same unit time to go through a rail unit, not depending on the types of the unit or the tramcar directions. After the tramcar starts on a rail unit on a “fun route”, it will come back to the same unit with the same running condition, sooner or later. The fun time T of a fun route is the number of time units that the tramcar takes for going around the route.
Of course, kids better enjoy layouts with longer fun time. Given a variety of rail units placed on a rectangular area, your job is to rotate the given rail units appropriately and to find the fun route with the longest fun time in the valid layouts.
For example, there is a fun route in Figure 10(b). Its fun time is 24. Let the toy tramcar start from B/M-end at (1, 2) toward (1, 3) and the states of all the switches are the through-states. It goes through (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (2, 5), (2, 4), (1, 4), (1, 3), (1, 2), (1, 1), (2, 1), (2, 2) and (1, 2). Here, the tramcar goes through (1, 2) with the same position and the same direction, but with the different states of the switches. Then the tramcar goes through (1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 4), (2, 5), (1, 5), (1, 4), (1, 3), (1, 2), (2, 2), (2, 1), (1, 1) and (1, 2). Here, the tramcar goes through (1, 2) again, but with the same switch states as the initial ones. Counting the rail units the tramcar visited, the tramcar should have run 24 units of time after its start, and thus the fun time is 24.
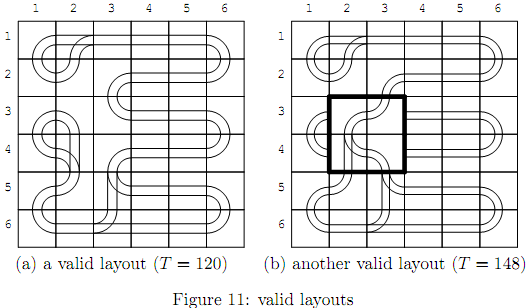
There may be many valid layouts with the given rail units. For example, a valid layout containing a fun route with the fun time 120 is shown in Figure 11(a). Another valid layout containing a fun route with the fun time 148 derived from that in Figure 11(a) is shown in Figure 11(b). The four rail units whose rotations are changed from Figure 11(a) are indicated by the thick lines.
A valid layout depicted in Figure 12(a) contains two fun routes, where one consists of the rail units (1, 1), (2, 1), (3, 1), (4, 1), (4, 2), (3, 2), (2, 2), (1, 2) with T = 8, and the other consists of all the remaining rail units with T = 18.
Another valid layout depicted in Figure 12(b) has two fun routes whose fun times are T = 12 and T = 20. The layout in Figure 12(a) is di?erent from that in Figure 12(b) at the eight rail units rotated by multiples of 90 degrees. There are other valid layouts with some rotations of rail units but there is no fun route with the fun time longer than 20, so that the longest fun time for this example (Figure 12) is 20.

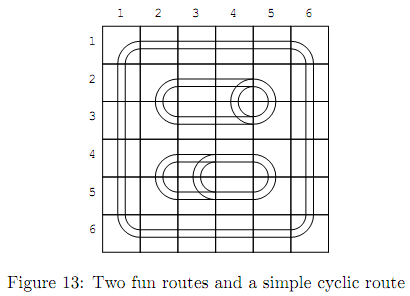
Note that there may be simple cyclic routes that do not go through any switches in a valid layout, which are not counted as the fun routes. In Figure 13, there are two fun routes and one simple cyclic route. Their fun times are 12 and 14, respectively. The required time for going around the simple cyclic route is 20 that is greater than fun times of the fun routes. However, the longest fun time is still 14.

A switch is either in “through” or “branching” state. When the tramcar comes from B/M-end, and if the switch is in the through-state, the tramcar goes through to S-end and the state changes to branching; if the switch is in the branching-state, it branches toward C-end and the state changes to through. When the tramcar comes from S-end or C-end, it goes out from B/M-end regardless of the state. The state does not change in this case.
Kids are given rail units of various types that fill a rectangle area of w * h, as shown in Figure 10(a). Rail units meeting at an edge of adjacent two frames are automatically connected. Each rail unit may be independently rotated around the center of its frame by multiples of 90 degrees in order to change the connection of rail units, but its position cannot be changed.
Kids should make “valid” layouts by rotating each rail unit, such as getting Figure 10(b) from Figure 10(a). A layout is valid when all rails at three ends of every switch are directly or indirectly connected to an end of another switch or itself. A layout in Figure 10(c) is invalid as well as Figure 10(a). Invalid layouts are frowned upon.

When a tramcar runs in a valid layout, it will eventually begin to repeat the same route forever. That is, we will eventually find the tramcar periodically comes to the same running condition, which is a triple of the tramcar position in the rectangle area, its direction, and the set of the states of all the switches.
A periodical route is a sequence of rail units on which the tramcar starts from a rail unit with a running condition and returns to the same rail unit with the same running condition for the first time. A periodical route through a switch or switches is called the “fun route”, since kids like the rattling sound the tramcar makes when it passes through a switch. The tramcar takes the same unit time to go through a rail unit, not depending on the types of the unit or the tramcar directions. After the tramcar starts on a rail unit on a “fun route”, it will come back to the same unit with the same running condition, sooner or later. The fun time T of a fun route is the number of time units that the tramcar takes for going around the route.
Of course, kids better enjoy layouts with longer fun time. Given a variety of rail units placed on a rectangular area, your job is to rotate the given rail units appropriately and to find the fun route with the longest fun time in the valid layouts.
For example, there is a fun route in Figure 10(b). Its fun time is 24. Let the toy tramcar start from B/M-end at (1, 2) toward (1, 3) and the states of all the switches are the through-states. It goes through (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (2, 5), (2, 4), (1, 4), (1, 3), (1, 2), (1, 1), (2, 1), (2, 2) and (1, 2). Here, the tramcar goes through (1, 2) with the same position and the same direction, but with the different states of the switches. Then the tramcar goes through (1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 4), (2, 5), (1, 5), (1, 4), (1, 3), (1, 2), (2, 2), (2, 1), (1, 1) and (1, 2). Here, the tramcar goes through (1, 2) again, but with the same switch states as the initial ones. Counting the rail units the tramcar visited, the tramcar should have run 24 units of time after its start, and thus the fun time is 24.
There may be many valid layouts with the given rail units. For example, a valid layout containing a fun route with the fun time 120 is shown in Figure 11(a). Another valid layout containing a fun route with the fun time 148 derived from that in Figure 11(a) is shown in Figure 11(b). The four rail units whose rotations are changed from Figure 11(a) are indicated by the thick lines.

A valid layout depicted in Figure 12(a) contains two fun routes, where one consists of the rail units (1, 1), (2, 1), (3, 1), (4, 1), (4, 2), (3, 2), (2, 2), (1, 2) with T = 8, and the other consists of all the remaining rail units with T = 18.
Another valid layout depicted in Figure 12(b) has two fun routes whose fun times are T = 12 and T = 20. The layout in Figure 12(a) is di?erent from that in Figure 12(b) at the eight rail units rotated by multiples of 90 degrees. There are other valid layouts with some rotations of rail units but there is no fun route with the fun time longer than 20, so that the longest fun time for this example (Figure 12) is 20.

Note that there may be simple cyclic routes that do not go through any switches in a valid layout, which are not counted as the fun routes. In Figure 13, there are two fun routes and one simple cyclic route. Their fun times are 12 and 14, respectively. The required time for going around the simple cyclic route is 20 that is greater than fun times of the fun routes. However, the longest fun time is still 14.

输入解释
The input consists of multiple datasets, followed by a line containing two zeros separated by a space. Each dataset has the following format.
w is the number of the rail units in a row, and h is the number of those in a column. aij (1 <= i <= h, 1 <= j <= w) is one of uppercase letters ‘S’, ‘C’, ‘L’ and ‘R’, which indicate the types of the rail unit at (i, j) position, i.e., straight, curve, left-switch and right-switch, respectively. Items in a line are separated by a space. You can assume that 2 <= w <= 6, 2 <= h <= 6 and the sum of the numbers of left-switches and right-switches is greater than or equal to 2 and less than or equal to 6.
w h
a11 ... a1w
...
ah1 ... ahw
w is the number of the rail units in a row, and h is the number of those in a column. aij (1 <= i <= h, 1 <= j <= w) is one of uppercase letters ‘S’, ‘C’, ‘L’ and ‘R’, which indicate the types of the rail unit at (i, j) position, i.e., straight, curve, left-switch and right-switch, respectively. Items in a line are separated by a space. You can assume that 2 <= w <= 6, 2 <= h <= 6 and the sum of the numbers of left-switches and right-switches is greater than or equal to 2 and less than or equal to 6.
输出解释
For each dataset, an integer should be printed that indicates the longest fun time of all the fun routes in all the valid layouts with the given rail units. When there is no valid layout according to the given rail units, a zero should be printed.
输入样例
5 2 C L S R C C C S C C 6 4 C C C C C C S L R R C S S S S L C S C C C C C C 6 6 C L S S S C C C C S S C C C C S S C C L C S S C C C L S S C C S L S S C 6 6 C S S S S C S C S L C S S C S R C S S C L S C S S C R S C S C S S S S C 4 4 S C C S S C L S S L C S C C C C 6 4 C R S S L C C R L R L C C S C C S C C S S S S C 0 0
输出样例
24 20 148 14 0 178
最后修改于 2020-10-29T07:12:10+00:00 由爬虫自动更新
共提交 0 次
通过率 --%
| 时间上限 | 内存上限 |
| 1000 | 65536 |
登陆或注册以提交代码