当前你的浏览器版本过低,网站已在兼容模式下运行,兼容模式仅提供最小功能支持,网站样式可能显示不正常。
请尽快升级浏览器以体验网站在线编辑、在线运行等功能。
3315:Roofing It
题目描述
Bill Eaves owns the Shingle Minded roofing company which is a sub-contracting firm specializing in putting roofs on buildings. Often, Bill will receive a design for a roof from some young hot-shot architect which, though it may have some aesthetic appeal, is totally impractical. In these cases, Bill will begin negotiations with the architect and the client to find a simpler design. Bill's only concern is that the roof be convex, to allow rain, snow and frisbees to roll off easily. The architect's main concern is that the maximum height between his original roof and the compromise roof be as small as possible. The client's main concern is to get out of this meeting as soon as possible and get back to watching TV.
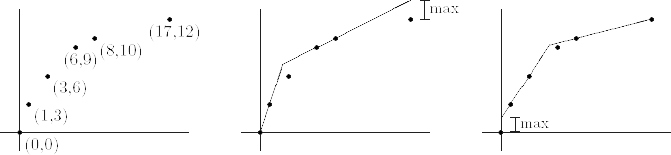
The architect's plans for the roof come in the form of a series of n points (xi, yi) specifying the outline of the roof as seen from the side of the house. The roofs are always symmetrical, so the architect only shows the front side of the roof (from its start at the front of the house to its peak). Once Bill gets these plans and a decision is made on how many sections the convex roof should have, he must decide how to place the sections so as to 1) make sure that all the original (xi, yi) points lie on or below the new roof, and 2) to minimize the maximum vertical distance between any of the original (xi, yi) points and the new roof. All sections must lie on at least two of the initial points specified by the architect. An example is shown below. On the left are the initial points from the architect. The next two pictures show an approximation of the roof using only two sections. While both of these are convex, the second of the two is the one which minimizes the maximum distance.
输入解释
Input will consist of multiple test cases. Each case will begin with two positive integers n and k (2 ≤ n ≤ 100, 1 ≤ k < n) indicating the number of points used in the original roof plan and the number of sections used in the compromise roof. These will be followed by n lines each containing two floating points numbers xi yi, specifying the n points in the roof plan. These values will be given in increasing order of x, and the last point will be guaranteed to have the highest y value of any of the points. All values will be between 0.0 and 10000.0. The last case is followed by a line containing 0 0 which indicates end-of-input and should not be processed.
输出解释
For each test case, output the maximum distance between the best compromise roof and the initial points, rounded to the nearest thousandth.
输入样例
6 2 0.0 0.0 1.0 3.0 3.0 6.0 6.0 9.0 8.0 10.0 17.0 12.0 0 0
输出样例
1.500
最后修改于 2020-10-29T06:58:23+00:00 由爬虫自动更新
共提交 0 次
通过率 --%
| 时间上限 | 内存上限 |
| 2000 | 65536 |