当前你的浏览器版本过低,网站已在兼容模式下运行,兼容模式仅提供最小功能支持,网站样式可能显示不正常。
请尽快升级浏览器以体验网站在线编辑、在线运行等功能。
2917:Diophantus of Alexandria
题目描述
Diophantus of Alexandria was an Egypt mathematician living in Alexandria. He was one of the first mathematicians to study equations where variables were restricted to integral values. In honor of him, these equations are commonly called Diophantine equations. One of the most famous Diophantine equation is xn + yn = zn. Fermat suggested that for n > 2, there are no solutions with positive integral values for x, y and z. A proof of this theorem (called Fermat’s last theorem) was found only recently by Andrew Wiles.
Consider the following Diophantine equation:
 (1)
(1)
Diophantus is interested in the following question: for a given n, how many distinct solutions (i. e., solutions satisfying x ≤ y) does equation (1) have? For example, for n = 4, there are exactly three distinct solutions:
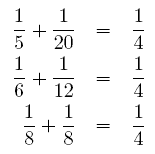
Clearly, enumerating these solutions can become tedious for bigger values of n. Can you help Diophantus compute the number of distinct solutions for big values of n quickly?
输入解释
The first line contains the number of scenarios. Each scenario consists of one line containing a single number n (1 ≤ n ≤ 109).
输出解释
The output for every scenario begins with a line containing “Scenario #i:”, where i is the number of the scenario starting at 1. Next, print a single line with the number of distinct solutions of equation (1) for the given value of n. Terminate each scenario with a blank line.
输入样例
2 4 1260
输出样例
Scenario #1: 3 Scenario #2: 113
最后修改于 2020-10-29T06:47:29+00:00 由爬虫自动更新
共提交 0 次
通过率 --%
| 时间上限 | 内存上限 |
| 1000 | 65536 |