当前你的浏览器版本过低,网站已在兼容模式下运行,兼容模式仅提供最小功能支持,网站样式可能显示不正常。
请尽快升级浏览器以体验网站在线编辑、在线运行等功能。
2784:Buy or Build
题目描述
World Wide Networks (WWN) is a leading company that operates large telecommunication networks. WWN would like to setup a new network in Borduria, a nice country that recently managed to get rid of its military dictator Kurvi-Tasch and which is now seeking for investments of international companies (for a complete description of Borduria, have a look to the following Tintin albums ``King Ottokar's Sceptre", ``The Calculus Affair" and ``Tintin and the Picaros"). You are requested to help WWN todecide how to setup its network for a minimal total cost.
Problem
There are several local companies running small networks (called subnetworks in the following) that partially cover the n largest cities of Borduria. WWN would like to setup a network that connects all n cities. To achieve this, it can either build edges between cities from scratch or it can buy one or several subnetworks from local companies. You are requested to help WWN to decide how to setup its network for a minimal total cost.
You have to decide which existing networks you buy and which edges you setup so that the total cost is minimal. Note that the number of existing networks is always very small (typically smaller than 8).
A 115 Cities Instance
Consider a 115 cities instance of the problem with 4 subnetworks (the 4 first graphs in Figure 1). As mentioned earlier the exact shape of a subnetwork is not relevant still, to keep figures easy to read, we have assumed an arbitrary tree like structure for each subnetworks. The bottom network in Figure 1 corresponds to the solution in which the first and the third networks have been bought. Thin edges correspond to edges build from scratch while thick edges are those from one of the initial networks.
Problem
There are several local companies running small networks (called subnetworks in the following) that partially cover the n largest cities of Borduria. WWN would like to setup a network that connects all n cities. To achieve this, it can either build edges between cities from scratch or it can buy one or several subnetworks from local companies. You are requested to help WWN to decide how to setup its network for a minimal total cost.
- All n cities are located by their two-dimensional Cartesian coordinates.
- There are q existing subnetworks. If q>=1 then each subnetwork c ( 1<=c<=q ) is defined by a set of interconnected cities (the exact shape of a subnetwork is not relevant to our problem).
- A subnetwork c can be bought for a total cost wc and it cannot be split (i.e., the network cannot be fractioned).
- To connect two cities that are not connected through the subnetworks bought, WWN has to build an edge whose cost is exactly the square of the Euclidean distance between the cities.
You have to decide which existing networks you buy and which edges you setup so that the total cost is minimal. Note that the number of existing networks is always very small (typically smaller than 8).
A 115 Cities Instance
Consider a 115 cities instance of the problem with 4 subnetworks (the 4 first graphs in Figure 1). As mentioned earlier the exact shape of a subnetwork is not relevant still, to keep figures easy to read, we have assumed an arbitrary tree like structure for each subnetworks. The bottom network in Figure 1 corresponds to the solution in which the first and the third networks have been bought. Thin edges correspond to edges build from scratch while thick edges are those from one of the initial networks.
输入解释
The first line contains the number n of cities in the country ( 1<=n<=1000 ) followed by the number q of existing subnetworks ( 0<=q<=8 ). Cities are identified by a unique integer value ranging from 1 to n . The first line is followed by q lines (one per subnetwork), all of them following the same pattern: The first integer is the number of cities in the subnetwork. The second integer is the the cost of the subnetwork (not greater than 2 x 106 ). The remaining integers on the line (as many as the number of cities in the subnetwork) are the identifiers of the cities in the subnetwork. The last part of the file contains n lines that provide the coordinates of the cities (city 1 on the first line, city 2 on the second one, etc). Each line is made of 2 integer values (ranging from 0 to 3000) corresponding to the integer coordinates of the city.
输出解释
Your program has to write the optimal total cost to interconnect all cities.
输入样例
7 3 2 4 1 2 3 3 3 6 7 3 9 2 4 5 0 2 4 0 2 0 4 2 1 3 0 5 4 4
输出样例
17
提示
Sample Explanation: The above instance is shown in Figure 2. An optimal solution is described in Figure 3 (thick edges come from an existing network while thin edges have been setup from scratch).
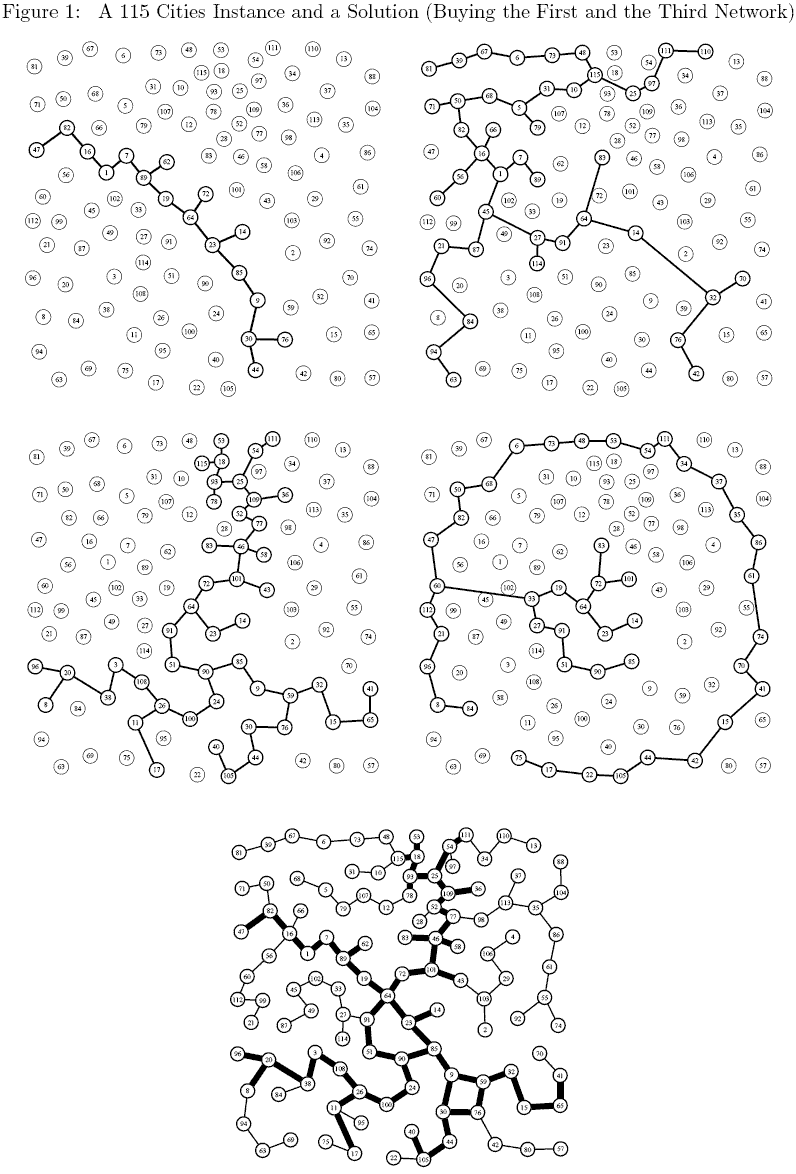
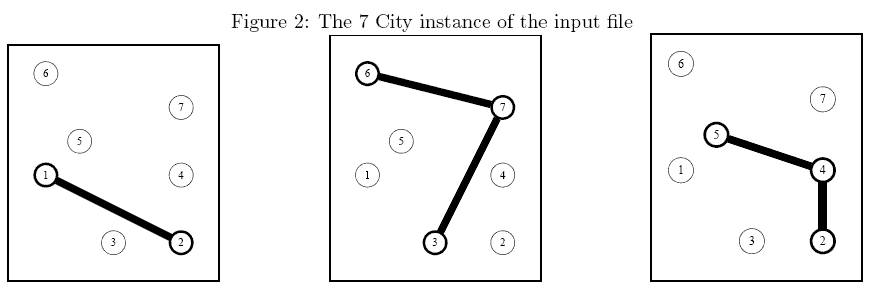
Figure 3: An optimal solution of the 7 City instance in which which the first and second existing networkshave been bought while two extra edges (1, 5) and (2, 4)
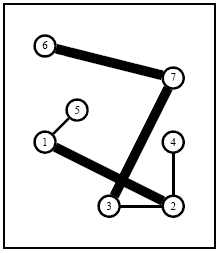


Figure 3: An optimal solution of the 7 City instance in which which the first and second existing networkshave been bought while two extra edges (1, 5) and (2, 4)

最后修改于 2020-10-29T06:43:49+00:00 由爬虫自动更新
共提交 0 次
通过率 --%
| 时间上限 | 内存上限 |
| 2000 | 65536 |
登陆或注册以提交代码