当前你的浏览器版本过低,网站已在兼容模式下运行,兼容模式仅提供最小功能支持,网站样式可能显示不正常。
请尽快升级浏览器以体验网站在线编辑、在线运行等功能。
2742:Organize Your Train
题目描述
In the good old Hachioji railroad station located in the west of Tokyo, there are several parking lines, and lots of freight trains come and go every day.
All freight trains travel at night, so these trains containing various types of cars are settled in your parking lines early in the morning. Then, during the daytime, you must reorganize cars in these trains according to the request of the railroad clients, so that every line contains the "right" train, i.e. the right number of cars of the right types, in the right order.
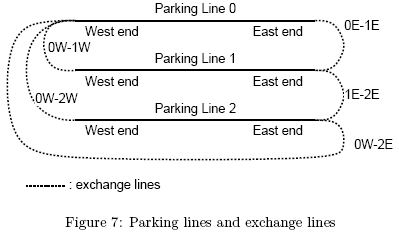
As shown in Figure 7, all parking lines run in the East-West direction. There are exchange lines connecting them through which you can move cars. An exchange line connects two ends of different parking lines. Note that an end of a parking line can be connected to many ends of other lines. Also note that an exchange line may connect the East-end of a parking line and the West-end of another.
Cars of the same type are not discriminated between each other. The cars are symmetric, so directions of cars don't matter either.
You can divide a train at an arbitrary position to make two sub-trains and move one of them through an exchange line connected to the end of its side. Alternatively, you may move a whole train as is without dividing it. Anyway, when a (sub-) train arrives at the destination parking line and the line already has another train in it, they are coupled to form a longer train.
Your superautomatic train organization system can do these without any help of locomotive engines. Due to the limitation of the system, trains cannot stay on exchange lines; when you start moving a (sub-) train, it must arrive at the destination parking line before moving another train.
In what follows, a letter represents a car type and a train is expressed as a sequence of letters. For example in Figure 8, from an initial state having a train "aabbccdee" on line 0 and no trains on other lines, you can make "bbaadeecc" on line 2 with the four moves shown in the figure.
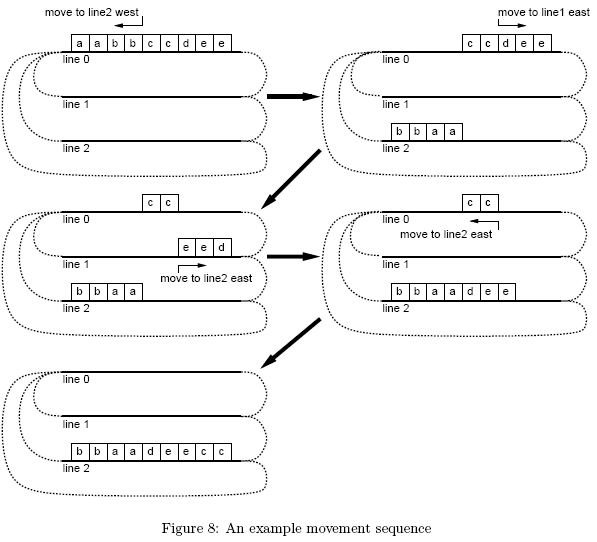
To cut the cost out, your boss wants to minimize the number of (sub-) train movements. For example, in the case of Figure 8, the number of movements is 4 and this is the minimum.
Given the configurations of the train cars in the morning (arrival state) and evening (departure state), your job is to write a program to find the optimal train reconfiguration plan.
All freight trains travel at night, so these trains containing various types of cars are settled in your parking lines early in the morning. Then, during the daytime, you must reorganize cars in these trains according to the request of the railroad clients, so that every line contains the "right" train, i.e. the right number of cars of the right types, in the right order.
As shown in Figure 7, all parking lines run in the East-West direction. There are exchange lines connecting them through which you can move cars. An exchange line connects two ends of different parking lines. Note that an end of a parking line can be connected to many ends of other lines. Also note that an exchange line may connect the East-end of a parking line and the West-end of another.

Cars of the same type are not discriminated between each other. The cars are symmetric, so directions of cars don't matter either.
You can divide a train at an arbitrary position to make two sub-trains and move one of them through an exchange line connected to the end of its side. Alternatively, you may move a whole train as is without dividing it. Anyway, when a (sub-) train arrives at the destination parking line and the line already has another train in it, they are coupled to form a longer train.
Your superautomatic train organization system can do these without any help of locomotive engines. Due to the limitation of the system, trains cannot stay on exchange lines; when you start moving a (sub-) train, it must arrive at the destination parking line before moving another train.
In what follows, a letter represents a car type and a train is expressed as a sequence of letters. For example in Figure 8, from an initial state having a train "aabbccdee" on line 0 and no trains on other lines, you can make "bbaadeecc" on line 2 with the four moves shown in the figure.

To cut the cost out, your boss wants to minimize the number of (sub-) train movements. For example, in the case of Figure 8, the number of movements is 4 and this is the minimum.
Given the configurations of the train cars in the morning (arrival state) and evening (departure state), your job is to write a program to find the optimal train reconfiguration plan.
输入解释
The input consists of one or more datasets. A dataset has the following format:
x y
p1P1 q1Q1
p2P2 q2Q2 ...
pyPy qyQy
s0
s1 ...
sx-1
t0
t1 ...
tx-1
x is the number of parking lines, which are numbered from 0 to x-1. y is the number of exchange lines. Then y lines of the exchange line data follow, each describing two ends connected by the exchange line; pi and qi are integers between 0 and x-1 which indicate parking line numbers, and Pi and Qi are either "E" (East) or "W" (West) which indicate the ends of the parking lines.
Then x lines of the arrival (initial) configuration data, s0, ... , sx-1, and x lines of the departure (target) configuration data, t0, ... tx-1, follow. Each of these lines contains one or more lowercase letters "a", "b", ..., "z", which indicate types of cars of the train in the corresponding parking line, in west to east order, or alternatively, a single "-" when the parking line is empty.
You may assume that x does not exceed 4, the total number of cars contained in all the trains does not exceed 10, and every parking line has sufficient length to park all the cars.
You may also assume that each dataset has at least one solution and that the minimum number of moves is between one and six, inclusive.
Two zeros in a line indicate the end of the input.
x y
p1P1 q1Q1
p2P2 q2Q2 ...
pyPy qyQy
s0
s1 ...
sx-1
t0
t1 ...
tx-1
x is the number of parking lines, which are numbered from 0 to x-1. y is the number of exchange lines. Then y lines of the exchange line data follow, each describing two ends connected by the exchange line; pi and qi are integers between 0 and x-1 which indicate parking line numbers, and Pi and Qi are either "E" (East) or "W" (West) which indicate the ends of the parking lines.
Then x lines of the arrival (initial) configuration data, s0, ... , sx-1, and x lines of the departure (target) configuration data, t0, ... tx-1, follow. Each of these lines contains one or more lowercase letters "a", "b", ..., "z", which indicate types of cars of the train in the corresponding parking line, in west to east order, or alternatively, a single "-" when the parking line is empty.
You may assume that x does not exceed 4, the total number of cars contained in all the trains does not exceed 10, and every parking line has sufficient length to park all the cars.
You may also assume that each dataset has at least one solution and that the minimum number of moves is between one and six, inclusive.
Two zeros in a line indicate the end of the input.
输出解释
For each dataset, output the number of moves for an optimal reconfiguration plan, in a separate line.
输入样例
3 5 0W 1W 0W 2W 0W 2E 0E 1E 1E 2E aabbccdee - - - - bbaadeecc 3 3 0E 1W 1E 2W 2E 0W aabb bbcc aa bbbb cc aaaa 3 4 0E 1W 0E 2E 1E 2W 2E 0W ababab - - aaabbb - - 0 0
输出样例
4 2 5
最后修改于 2020-10-29T06:41:15+00:00 由爬虫自动更新
共提交 0 次
通过率 --%
| 时间上限 | 内存上限 |
| 15000 | 262144 |
登陆或注册以提交代码