当前你的浏览器版本过低,网站已在兼容模式下运行,兼容模式仅提供最小功能支持,网站样式可能显示不正常。
请尽快升级浏览器以体验网站在线编辑、在线运行等功能。
4225:Simulation?
题目描述
A computer simulation, a computer model, or a computational model is a computer program, or network of computers, that attempts to simulate an abstract model of a particular system. Computer simulations have become a useful part of mathematical modeling of many natural systems in physics, astrophysics, chemistry and biology, human systems in economics, psychology, social science, and engineering, of course, also computer.
“Fundamentals of compiling” is an important course for computer science students. In this course, most of us are asked to write a compiler to simulate how a programming language executes. Today, boring iSea invites a new programming language, whose name is Abnormal Cute Micro (ACM) language, and, YOU are assigned the task to write a compiler for it.
ACM language only contains two kinds of variables and a few kinds of operations or functions, and here are some BNF-like rules for ACM.


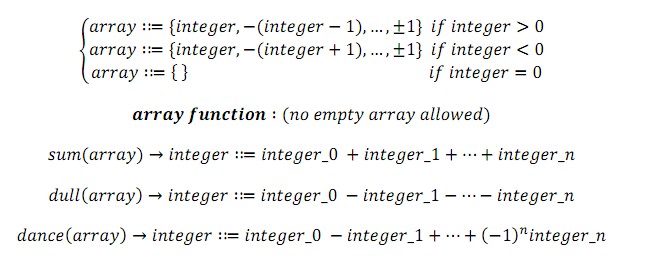
Also, here is some explanation for these rules:
1) In ACM expressions, use exactly one blank to separate variables and operators, and as the rule indicates, the operator should apply right to left, for example, the result of “1 - 2 - 3" should be 2.
2) In the build function, use exactly one blank to separate integers, too.
3) Beside there are brackets in function, no other bracket exists.
4) All the variables are conformable, and never exceed 10000.
Given an ACM expression, your task is output its value. If the result is a integer, just report it, otherwise report an array using the format “{integer_0, integer_1, … , integer_n}”.
“Fundamentals of compiling” is an important course for computer science students. In this course, most of us are asked to write a compiler to simulate how a programming language executes. Today, boring iSea invites a new programming language, whose name is Abnormal Cute Micro (ACM) language, and, YOU are assigned the task to write a compiler for it.
ACM language only contains two kinds of variables and a few kinds of operations or functions, and here are some BNF-like rules for ACM.



Also, here is some explanation for these rules:
1) In ACM expressions, use exactly one blank to separate variables and operators, and as the rule indicates, the operator should apply right to left, for example, the result of “1 - 2 - 3" should be 2.
2) In the build function, use exactly one blank to separate integers, too.
3) Beside there are brackets in function, no other bracket exists.
4) All the variables are conformable, and never exceed 10000.
Given an ACM expression, your task is output its value. If the result is a integer, just report it, otherwise report an array using the format “{integer_0, integer_1, … , integer_n}”.
输入解释
The first line contains a single integer T, indicating the number of test cases.
Each test case includes a string indicating an valid ACM expression you have to process.
Technical Specification
1. 1 <= T <= 100
2. 1 <= |S| <= 100, |S| indicating the length of the string.
Each test case includes a string indicating an valid ACM expression you have to process.
Technical Specification
1. 1 <= T <= 100
2. 1 <= |S| <= 100, |S| indicating the length of the string.
输出解释
For each test case, output the case number first, then the result variable.
输入样例
10 1 + 1 1 - 2 - 3 dance(3) vary(2) * 2 vary(sum(dance(5) - 1)) dance(dance(-3)) 1 - 2 - 3 * vary(dull(build(1 2 3))) dance(dance(dance(dance(dance(2))))) sum(vary(100)) - sum(build(3038)) build(sum(vary(2)) dull(build(1 0)) 2 dull(dance(2))) - build(1 1 1 1)
输出样例
Case 1: 2
Case 2: 2
Case 3: {3, -2, 1}
Case 4: {2, 4}
Case 5: {2, 1}
Case 6: -4
Case 7: {2, 5}
Case 8: {4, -3, 2, -1}
Case 9: 2012
Case 10: {2, 0, 1, 2}
来自杭电HDUOJ的附加信息
| Author | iSea@WHU |
| Recommend | lcy |
最后修改于 2020-10-25T23:11:28+00:00 由爬虫自动更新
共提交 0 次
通过率 --%
| 时间上限 | 内存上限 |
| 2000/1000MS(Java/Others) | 65536/65536K(Java/Others) |
登陆或注册以提交代码